Calcined Clay Pozzolan's Influence and Aggregate Size on the Properties of Pervious Concrete
Pervious concrete is a permeable material used in pavement and other construction applications. It is made up of cement, water, and coarse aggregate, with little to no fine aggregate or sand. The result is a porous material that allows water to infiltrate the surface and recharge groundwater and is increasingly being used as an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional concrete in many applications. However, the mechanical and durability properties of pervious concrete can be limited, making it less suitable for some applications.
In a recent study titled "Influence of Calcined Clay Pozzolan and Aggregate Size on the Mechanical and Durability Properties of Pervious Concrete," published by Kwabena Boakye and Morteza Khorami. The researchers sought to address some of these limitations by exploring the impact of calcined clay pozzolan and aggregate size on the properties of pervious concrete.
Calcined clay pozzolan is a supplementary cementitious material that is made by calcining clay at high temperatures. It can be used as a partial replacement for cement in concrete to improve its mechanical and durability properties. In the study, the researchers replaced a portion of the cement with calcined clay pozzolan and examined the effect on the compressive strength, permeability, and water absorption resistance of pervious concrete.
The researchers also looked at the impact of varying the aggregate size on these properties. They tested three different sizes of coarse aggregate, ranging from 9.5 mm to 19 mm, to determine the optimal size for improving the properties of pervious concrete.
The study found that incorporating calcined clay pozzolan into pervious concrete increased its compressive strength and water absorption resistance while decreasing its permeability. This is because calcined clay pozzolan reacts with the calcium hydroxide in the cement to form additional calcium silicate hydrates, which are responsible for the strength of the material.
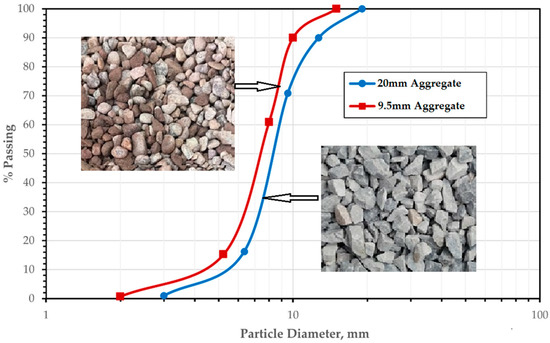
IMAGE - Particle size distribution of coarse aggregates.
Additionally, increasing the size of the coarse aggregate resulted in an increase in compressive strength and permeability, but a decrease in water absorption resistance. This is because larger aggregate size leads to a higher porosity, which allows more water to infiltrate the surface.
The study's findings suggest that using calcined clay pozzolan as a partial replacement for cement and carefully selecting the size of the coarse aggregate can improve the mechanical and durability properties of pervious concrete. However, the researchers caution that optimizing the properties of pervious concrete requires a balance between permeability and durability.
The use of pervious concrete is gaining popularity in many construction applications due to its environmentally friendly nature. By improving the mechanical and durability properties of pervious concrete, it becomes a more viable option for a wider range of applications. The findings of this study contribute to the ongoing research on how to optimize pervious concrete for various construction purposes.
In conclusion, the use of calcined clay pozzolan and careful selection of aggregate size can significantly impact the mechanical and durability properties of pervious concrete. The findings of this study provide valuable insight into how to optimize this material for various construction applications, while maintaining its environmentally friendly properties.
To read the full study, click here.
